一、简单介绍
这是其他几篇关于并行的文章:
本篇讲如何在 Python 中如何实现多个任务的并行(多进程)。在 Python 中,multiprocessing 模块提供了一个 Process 类来代表一个进程对象,而在 Fortran 的 OpenMP 中是通过启动“线程”来实现并行。补充说明:在Python中,有 threading 模块可以实现多线程的并行,也是比较常用的,参考:常用的Python软件包。
multiprocessing 文档:https://docs.python.org/3/library/multiprocessing.html。
进程并行和线程并行是实现多任务并行常见的两种方法。打开电脑的任务管理器(底部栏右击),在应用程序旁边就是“进程”。运行本文的例子程序时,可以发现 Python 的 multiprocessing 会产生多个“进程”,实现多个任务的并行,截图如下:
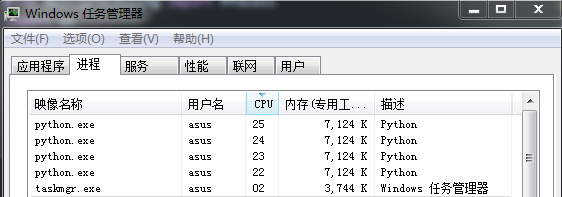
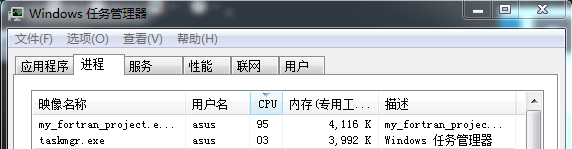
而在运行 Fortran 的 OpenMP 例子时,单个进程占了近 100%CPU(四个核,一个核为25%),也就是OpenMP 通过产生多个“线程”,分给指定 CPU 运行,实现多任务的并行,截图如下:
二、测试例子(Process 类)
以下是整理的一个Python多任务并行(multiprocessing 模块 Process 类)的测试例子:
"""
This code is supported by the website: https://www.guanjihuan.com
The newest version of this code is on the web page: https://www.guanjihuan.com/archives/4536
"""
import multiprocessing
import os
import time
def run_proc(name): # 要执行的代码
start_time = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(2)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print ('Process id running on %s = %s' % (name, os.getpid()), '; running time = %s' % (end_time-start_time))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 串行
print('串行程序')
print('Process id = %s.' % os.getpid())
start_time = time.perf_counter()
run_proc('job1')
run_proc('job2')
run_proc('job3')
run_proc('job4')
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('CPU执行时间(s)=', (end_time-start_time), '\n')
# 并行
print('并行程序')
print('Process id = %s.' % os.getpid())
start_time = time.perf_counter()
p1 = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_proc, args=('job1',))
p2 = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_proc, args=('job2',))
p3 = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_proc, args=('job3',))
p4 = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_proc, args=('job4',))
p1.start()
p2.start()
p3.start()
p4.start()
p1.join() # join()方法可以等待子进程结束后再继续往下运行
p2.join()
p3.join()
p4.join()
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('运行时间(s)=', (end_time-start_time))运行结果:
串行程序
Process id = 37156.
Process id running on job1 = 37156 ; running time = 2.0097683
Process id running on job2 = 37156 ; running time = 2.0110964
Process id running on job3 = 37156 ; running time = 2.0105541000000002Process id running on job4 = 37156 ; running time = 2.0046176000000004CPU执行时间(s)= 8.0375171
并行程序
Process id = 37156.
Process id running on job4 = 38820 ; running time = 2.0051369
Process id running on job3 = 21208 ; running time = 2.0048537
Process id running on job1 = 29340 ; running time = 2.0072364
Process id running on job2 = 34028 ; running time = 2.0072584
运行时间(s)= 2.1242947Python 运行速度会比 Fortran 慢,但熟悉后写起来挺方便的。在科学计算中,如果想用 Python 写代码,又想赶进度,除了手动操作并行外,还可以用上以上这种并行方法。尤其是当使用超算时,如果没有使用多任务并行,选择多个核的速度和选择一个核的运行的速度相差不多的,这时候如果仍然选择多个核(如12个核)进行运算,就很有可能会极大地浪费超算资源和科研经费。
三、使用字典传入参数(Process 类)
使用字典传入参数会更灵活些,不一定要按顺序传入参数,这样可以跳过一些默认的参数。
代码例子如下:
"""
This code is supported by the website: https://www.guanjihuan.com
The newest version of this code is on the web page: https://www.guanjihuan.com/archives/4536
"""
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
import time
def run_proc(name, a=0, b=-1): # 要执行的代码
start_time = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(2)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print ('Process id running on %s = %s' % (name, os.getpid()), f'; Values: a={a}, b={b}', '; running time = %s' % (end_time-start_time))
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('并行程序')
print('Process id = %s.' % os.getpid())
start_time = time.perf_counter()
p1 = Process(target=run_proc, kwargs={'name':'job1', 'a':10, 'b':100})
p2 = Process(target=run_proc, kwargs={'name':'job2', 'a':20})
p3 = Process(target=run_proc, kwargs={'name':'job3', 'b':300})
p4 = Process(target=run_proc, kwargs={'name':'job4'})
p1.start()
p2.start()
p3.start()
p4.start()
p1.join() # join()方法可以等待子进程结束后再继续往下运行
p2.join()
p3.join()
p4.join()
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('运行时间(s)=', (end_time-start_time))运行结果:
并行程序
Process id = 1440.
Process id running on job1 = 40524 ; Values: a=10, b=100 ; running time = 2.0056711000000003
Process id running on job2 = 16872 ; Values: a=20, b=-1 ; running time = 2.0023163999999998
Process id running on job3 = 38816 ; Values: a=0, b=300 ; running time = 2.0142491000000002
Process id running on job4 = 396 ; Values: a=0, b=-1 ; running time = 2.0081636
运行时间(s)= 2.1090617000000003四、循环参数实现(Process 类)
"""
This code is supported by the website: https://www.guanjihuan.com
The newest version of this code is on the web page: https://www.guanjihuan.com/archives/4536
"""
import multiprocessing
import os
import time
def run_proc(name): # 要执行的代码
start_time = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(2)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print ('Process id running on %s = %s' % (name, os.getpid()), '; running time = %s' % (end_time-start_time))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.perf_counter()
# 循环创建进程
processes = []
for i in range(4):
p = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_proc, args=(f'job{i}',))
processes.append(p)
p.start()
# 等待所有进程完成
for p in processes:
p.join()
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('运行时间(s)=', (end_time-start_time))运行结果:
Process id running on job0 = 25656 ; running time = 2.0011437
Process id running on job1 = 27852 ; running time = 2.0066053
Process id running on job3 = 30284 ; running time = 1.9998012000000003
Process id running on job2 = 20800 ; running time = 2.0012209999999997
运行时间(s)= 2.1166038五、使用共享内存实现返回函数值(Process 类)
如果是想返回函数值,可通过共享内存Value或Array来实现,参考资料为[1]。这里给出一个例子:
"""
This code is supported by the website: https://www.guanjihuan.com
The newest version of this code is on the web page: https://www.guanjihuan.com/archives/4536
"""
import multiprocessing
def run_proc(name, a, num): # 要执行的代码
num.value = a
if __name__ == '__main__':
num1 = multiprocessing.Value('d', 0.0) # 共享内存
num2 = multiprocessing.Value('d', 0.0) # 共享内存
p1 = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_proc, args=('job1', 100, num1))
p2 = multiprocessing.Process(target=run_proc, args=('job2', 200, num2))
p1.start()
p2.start()
p1.join()
p2.join()
print(num1.value)
print(num2.value)运行结果:
100.0
200.0另外,也可以通过写入文件和读取文件来实现。
六、使用 Process 的一个应用例子(手动分配任务)
multiprocessing.Process 的一个应用的例子如下(使用开源软件包:https://py.guanjihuan.com):
"""
This code is supported by the website: https://www.guanjihuan.com
The newest version of this code is on the web page: https://www.guanjihuan.com/archives/4536
"""
import multiprocessing
import os
import time
import numpy as np
import guan
def main(parameter_array, task_index):
print ('Process id = %s' % (os.getpid()))
result_array = []
for parameter in parameter_array:
result = parameter*2
result_array.append(result)
time.sleep(np.random.uniform(1,10))
guan.write_one_dimensional_data(parameter_array, result_array, filename='task_index='+str(task_index))
if __name__ == '__main__':
task_num = 4
parameter_array_all = np.arange(0, 17, 1)
start_time = time.perf_counter()
process_array = []
for task_index in range(task_num):
parameter_array = guan.preprocess_for_parallel_calculations(parameter_array_all, task_num, task_index)
process_array.append(multiprocessing.Process(target=main, args=(parameter_array, task_index)))
for process in process_array: # 运行子进程
process.start()
for process in process_array: # 等待子进程完成
process.join()
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('运行时间=', (end_time-start_time))
# 合并数据
f = open('result.txt', 'w')
for task_index in range(task_num):
with open('task_index='+str(task_index)+'.txt', 'r') as f0:
text = f0.read()
f.write(text)
f.close()运行结果:
Process id = 5356
Process id = 36908
Process id = 39844
Process id = 34404
运行时间= 9.2735009七、使用 Pool 自动分配任务并行
Pool 复用进程,适合大量小任务,且会自动分配任务;而Process 每次创建新进程,适合少量大任务。
这边是一个 multiprocessing.Pool 的例子:
"""
This code is supported by the website: https://www.guanjihuan.com
The newest version of this code is on the web page: https://www.guanjihuan.com/archives/4536
"""
import multiprocessing
import os
import time
def run_proc(name):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
time.sleep(2)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print ('Process id running on %s = %s' % (name, os.getpid()), '; running time = %s' % (end_time-start_time))
return name
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.perf_counter()
with multiprocessing.Pool() as pool:
results = pool.map(run_proc, [f"task {i}" for i in range(64)])
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print(results)
print(end_time - start_time)运行结果(16 个核):
Process id running on task 1 = 13892 ; running time = 2.003228
Process id running on task 0 = 19944 ; running time = 2.003348
Process id running on task 3 = 27180 ; running time = 1.9995218000000001
Process id running on task 2 = 33552 ; running time = 2.0030900999999997
Process id running on task 4 = 8636 ; running time = 2.0050225
Process id running on task 5 = 12680 ; running time = 2.0046258999999997
Process id running on task 6 = 28180 ; running time = 2.0012618
Process id running on task 7 = 3880 ; running time = 2.0113631
Process id running on task 9 = 3532 ; running time = 2.0165491
Process id running on task 8 = 17984 ; running time = 2.0181886
Process id running on task 10 = 31204 ; running time = 2.0106522
Process id running on task 12 = 30744 ; running time = 2.0032157
Process id running on task 11 = 28840 ; running time = 2.0088537
Process id running on task 14 = 19092 ; running time = 2.0014079000000002
Process id running on task 13 = 29724 ; running time = 2.0021406
Process id running on task 15 = 21764 ; running time = 2.0101902
Process id running on task 17 = 19944 ; running time = 2.0021476000000002
Process id running on task 18 = 27180 ; running time = 2.0020322
Process id running on task 19 = 33552 ; running time = 2.0019289999999996
Process id running on task 16 = 13892 ; running time = 2.0023773000000005
Process id running on task 20 = 8636 ; running time = 2.0074056999999996
Process id running on task 22 = 12680 ; running time = 2.0068569999999997
Process id running on task 21 = 28180 ; running time = 2.0069974
Process id running on task 23 = 3880 ; running time = 2.0091932000000003
Process id running on task 25 = 17984 ; running time = 2.002257
Process id running on task 24 = 3532 ; running time = 2.0024945
Process id running on task 26 = 31204 ; running time = 2.002265
Process id running on task 27 = 30744 ; running time = 2.0052756
Process id running on task 28 = 28840 ; running time = 2.0052457
Process id running on task 29 = 19092 ; running time = 2.0053474
Process id running on task 30 = 29724 ; running time = 2.0053769999999997
Process id running on task 31 = 21764 ; running time = 2.0039114999999996
Process id running on task 32 = 19944 ; running time = 2.0149236000000004
Process id running on task 34 = 33552 ; running time = 2.0148088999999993
Process id running on task 33 = 27180 ; running time = 2.0148668999999995
Process id running on task 35 = 13892 ; running time = 2.0147366
Process id running on task 36 = 8636 ; running time = 2.0115862999999994
Process id running on task 37 = 12680 ; running time = 2.0086575
Process id running on task 38 = 28180 ; running time = 2.0085722000000006
Process id running on task 39 = 3880 ; running time = 2.0103420000000005
Process id running on task 40 = 17984 ; running time = 2.0134245
Process id running on task 42 = 31204 ; running time = 2.0131613
Process id running on task 41 = 3532 ; running time = 2.0131658999999997
Process id running on task 44 = 28840 ; running time = 2.0103701000000003
Process id running on task 43 = 30744 ; running time = 2.0103565000000003
Process id running on task 46 = 29724 ; running time = 2.0107571
Process id running on task 45 = 19092 ; running time = 2.0108243999999997
Process id running on task 47 = 21764 ; running time = 2.0105155999999997
Process id running on task 50 = 27180 ; running time = 2.0111247999999993
Process id running on task 49 = 33552 ; running time = 2.0112127000000006
Process id running on task 51 = 13892 ; running time = 2.0110548999999995
Process id running on task 48 = 19944 ; running time = 2.0112600999999994
Process id running on task 52 = 8636 ; running time = 2.0108013000000007
Process id running on task 54 = 28180 ; running time = 2.0133741
Process id running on task 53 = 12680 ; running time = 2.0137150000000013
Process id running on task 55 = 3880 ; running time = 2.009126599999999
Process id running on task 57 = 31204 ; running time = 2.0058695
Process id running on task 56 = 17984 ; running time = 2.0061132000000006
Process id running on task 58 = 3532 ; running time = 2.0058581
Process id running on task 60 = 30744 ; running time = 2.0056417
Process id running on task 59 = 28840 ; running time = 2.0057498000000002
Process id running on task 61 = 29724 ; running time = 2.0068455000000007
Process id running on task 62 = 19092 ; running time = 2.0065433000000006
Process id running on task 63 = 21764 ; running time = 2.0050957999999994
['task 0', 'task 1', 'task 2', 'task 3', 'task 4', 'task 5', 'task 6', 'task 7', 'task 8', 'task 9', 'task 10', 'task 11', 'task 12', 'task 13', 'task 14', 'task 15', 'task 16', 'task 17', 'task 18', 'task 19', 'task 20', 'task 21', 'task 22', 'task 23', 'task 24', 'task 25', 'task 26', 'task 27', 'task 28', 'task 29', 'task 30', 'task 31', 'task 32', 'task 33', 'task 34', 'task 35', 'task 36', 'task 37', 'task 38', 'task 39', 'task 40', 'task 41', 'task 42', 'task 43', 'task 44', 'task 45', 'task 46', 'task 47', 'task 48', 'task 49', 'task 50', 'task 51', 'task 52', 'task 53', 'task 54', 'task 55', 'task 56', 'task 57', 'task 58', 'task 59', 'task 60', 'task 61', 'task 62', 'task 63']
8.323436975479126参考资料:
[1] 多进程
[2] multiprocessing --- 基于进程的并行
[3] 使用OMP_NUM_THREADS=1进行Python多处理
【说明:本站主要是个人的一些笔记和代码分享,内容可能会不定期修改。为了使全网显示的始终是最新版本,这里的文章未经同意请勿转载。引用请注明出处:https://www.guanjihuan.com】
你好,你这个函数是直接打印结果的。如果我的函数是要返回一个结果,那么并行要怎么获取函数值
可通过共享内存Value来实现。我在博文最后更新了内容,可以参考下。参考资料为[2],在网页中搜索“共享内存”,有对应的内容。